Data Format
Data Format allowed dataset formats as input
- The only accepted format is CSV, i.e. with a semi-column as separator, but two shapes are allowed: Samples in rows or Samples in columns, depending on how samples are organized within the file.
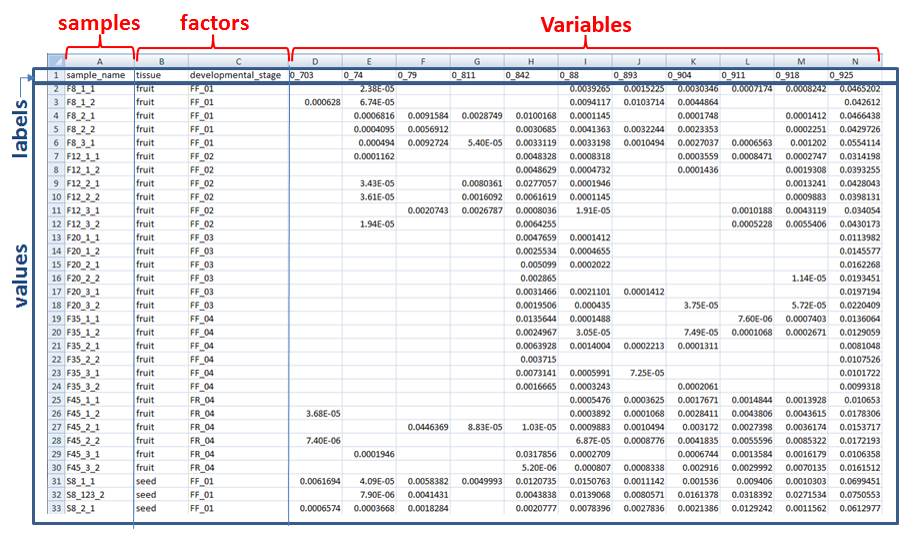
- Samples in rows means that there is a sample at each row, and its features in columns
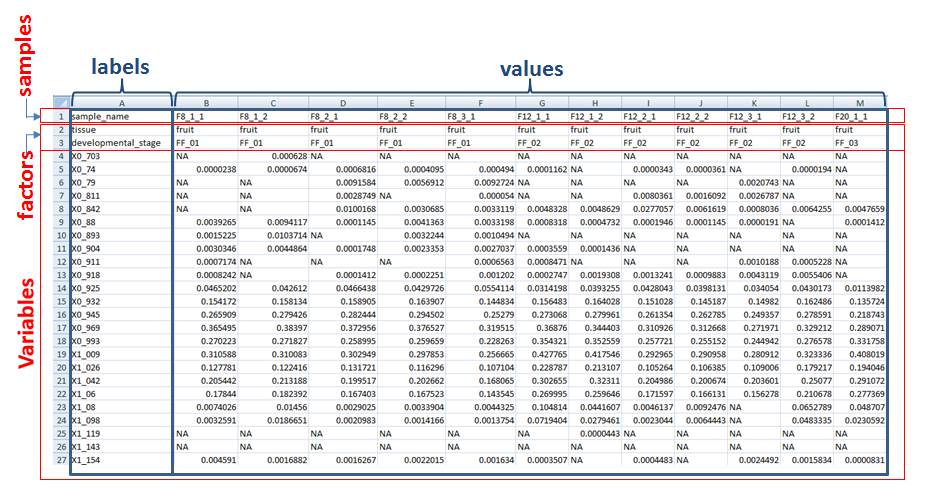
- Samples in columns means that there is a sample at each column, and its features in rows
Below, example of dataset with Two Factors (see Example of Dataset)
Samples in Rows
Samples in Columns
Advices & Tips concerning the input formatting
- Regarding the names about samples, factors and variables, avoid characters such as comma, blank or any special characters. Use only alphanumeric characters. If names are compliant to a nomenclature, use the underscore as separator rather than the dot.
- Be careful with the spreadsheets (especially with MS Excel) having had a lot of manipulations (copy-paste, cut, formula …), because some empty cells could be embedded into the CSV file during the exportation. The better is to copy-paste into a new spreadsheet only the data you want before exporting.
- If levels of a factor correspond to a time course (e.g. timestamps or development stages), take care to give them names so that their alphabetical order corresponds to the time course (e.g. if you have three time points given by 1, 5 and 10 hours, name them as “01”, “05” and “10”; otherwise the corresponding alphabetical order will be “1”, “10” and “5”). This tip is very useful for graphic representations, e.g. the boxplots.